Amino Acids
Baxter offers a portfolio of intravenous amino acid solutions specifically tailored to support growth in newborns and children and to meet the protein needs of adult patients.

Protein is critical not only for enabling growth and development in neonatal and pediatric patients,1 but also for maintaining lean body mass and supporting recovery in adults.2 When oral or enteral protein intake is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated, parenteral amino acid solutions can be used.2,13 Primene, Baxter’s 10% amino acid solution for neonatal and pediatric patients, contains a mixture of 20 essential, semi-essential, and non-essential amino acids and is designed to mimic cord plasma levels of preterm and fullterm infants.3,4 Synthamin, Baxter’s amino acid solution portfolio for adult patients, contains 15 essential and non-essential amino acids.5-10
See full prescribing information for Primene
See full prescribing information for Synthamin 9, 5.5%
See full prescribing information for Synthamin 14, 8.5%
See full prescribing information for Synthamin 17, 10.0%
See full prescribing information for Synthamin 9, 5.5% without electrolytes
See full prescribing information for Synthamin 14, 8.5% without electrolytes
See full prescribing information for Synthamin 17, 10.0% without electrolytes

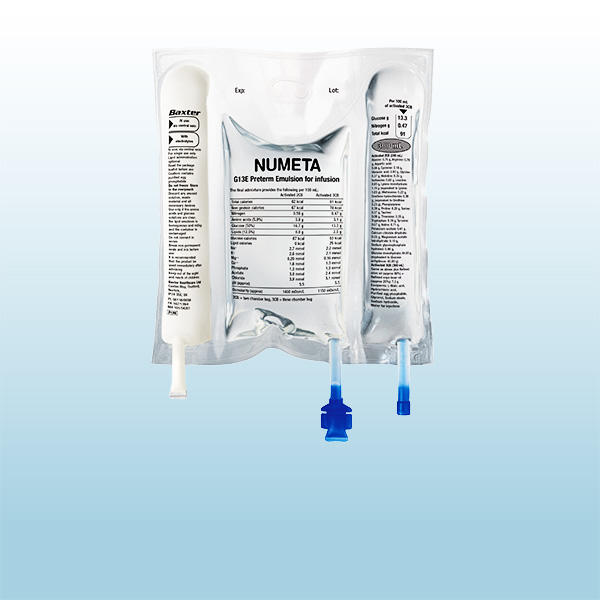
Primene 10% for neonatal and pediatric patients
Primene, a 20 amino acid solution, contains the highest cysteine, lysine, and ornithine content per gram of protein of all pediatric amino acid solutions and has been shown to promote growth in height and weight as well as psychomotor development in pediatric pateints.4,15-17,22 Provision of cysteine is necessary for production of glutathione, which is important in antioxidant defense and calcium homeostasis.11, 21 Primene has been meeting pediatric amino acids needs for over 35 years and is the same amino acid solution found in the Numeta portfolio of ready-to-use neonatal and pediatric three-chamber-bags.4,18,23,24

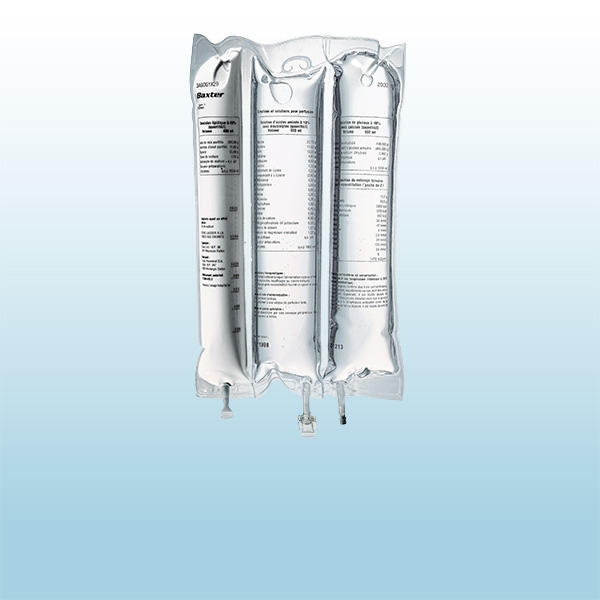
Synthamin for adult patients
For multiple decades, the portfolio of Synthamin amino acid solutions has provided a biologically available source of nitrogen for amino acid synthesis and is available in 5.5%, 8.5%, and 10% (with and without electrolytes) and a broad range of container sizes to meet patients’ varying needs. The Synthamin solutions are all composed of 15 essential and non-essential amino acids including the nine essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body.5-10
Synthamin is the same amino acid solution found in the OliClinomel portfolio of ready-to-use adult multi-chamber PN bags.5-10,19

Amino Acids
Download the Baxter Parenteral Nutrition Compatibility Guide for compounding compatibility and stability information.
Learn more about Clinical Nutrition

Related Products
Important safety information
This abbreviated summary of product characteristics (SPC) is intended for international use. Please note that it may differ from the licensed SPC in the country where you are practicing.
Therefore, please always consult your country-specific SPC or package leaflet.
NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
PRIMENE 10%
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each litre of the infusion solution contains:
L-Isoleucine 6.70g ; L-Leucine 10.00g ; L-Valine 7.60g ; L-Lysine 11.00g ; L-Methionine 2.40g ; L-Phenylalanine 4.20g ; L-Threonine 3.70g ; L-Tryptophan 2.00g ; L-Arginine 8.40g ; L-Histidine 3.80g ; L-Alanine 8.00g ; L-Aspartic Acid 6.00g ; L-Cysteine 1.89g; L-Glutamic Acid 10.00g ; Glycine 4.00g ; L-Proline 3.00g ; L-Serine 4.00g ;L-Tyrosine 0.45g ; L-Ornithine Hydrochloride 3.18g ; Taurine 0.60g
In a formulation also containing L-Malic acid, as described in the application.
CLINICAL PARTICULARS
Therapeutic Indications
Primene 10% is indicated in 1) children and infants 2) neonates, at term or premature, of normal or low birth weight when oral or enteral nutrition is impossible, insufficient or contraindicated.
Posology and Method of Administration
Dosage depends on the age, weight and protein catabolism of the child:
The usual range is: 15 – 35 ml of Primene 10%/kg/24 hours
The infusion rate should not exceed 0.05 ml/kg/min.
Recommended flow rates: Neonates and Infants: continuous infusion (over 24 hours).
Children: continuous infusion (over 24 hours) or cyclic infusion (over about 12 hours in 24).
The flow rate should be adjusted according to the dosage, the characteristics of the infusion solution, the total volume intake per 24 hours and the infusion duration.
Route of administration: Primene 10% alone should be administered in a central vein.
Primene 10% in co-administration or as a mixture should be administered according to the final osmolarity of the solution infused, in a peripheral or central vein.
Mode of administration: Primene 10% is usually administered with a source of energy appropriate for the needs of the child, either by co-administration or as a mixture.
Primene 10% may be included in the composition of nutritive mixtures combining carbohydrates, lipids, electrolytes, trace elements and vitamins when compatibility and stability are known.
Contraindications
Use in children with a congenital abnormality in the metabolism of one or more amino-acids.
Special Warnings and Special Precautions for Use
Primene 10% must be used with caution where severe restriction of water intake is necessary, e.g. cardiac, respiratory or renal failure. In cases of renal insufficiency, the nitrogen intake must be adjusted according to the Childs renal clearance. Caution should be exercised in cases of hepatic insufficiency with careful monitoring of blood ammonia levels. Careful monitoring of the infusion and of the clinical and biochemical conditions of the child is essential. In view of its osmolality, Primene 10% should not be infused alone into a superficial vein.
For a detailed posology, Special warnings and precautions, incompatibilities, interactions, pharmacological properties and pharmaceutical particulars, please refer to the full SPC. Medicinal products are subject to medical prescription
Jan 2020
Important safety information
SYNTHAMIN AMINO ACID INTRAVENOUS INFUSIONS PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Name and composition: Synthamin amino acid intravenous infusions.
|
Each one litre of solution contains : |
9 |
14 |
17 |
9 without electrolytes |
14 without electrolytes |
17 without electrolytes |
|
Total Amino Acids (% w/v) |
5.5 |
8.5 |
10.0 |
5.5 |
8.5 |
10.0 |
|
L-Leucine |
4.02g |
6.20g |
7.30g |
4.02g |
6.20g |
7.30g |
|
L-Phenylalanine |
3.08g |
4.76g |
5.60g |
3.08g |
4.76g |
5.60g |
|
L-Methionine |
2.20g |
3.40g |
4.00g |
2.20g |
3.40g |
4.00g |
|
L-Lysine |
3.19g |
4.93g |
5.80g |
3.19g |
4.93g |
5.80g |
|
L-Isoleucine |
3.30g |
5.10g |
6.00g |
3.30g |
5.10g |
6.00g |
|
L-Valine |
3.19g |
4.93g |
5.80g |
3.19g |
4.93g |
5.80g |
|
L-Histidine |
2.64g |
4.08g |
4.80g |
2.64g |
4.08g |
4.80g |
|
L-Threonine |
2.31g |
3.57g |
4.20g |
2.31g |
3.57g |
4.20g |
|
L-Tryptophan |
0.99g |
1.53g |
1.80g |
0.99g |
1.53g |
1.80g |
|
L-Alanine |
11.38g |
17.60g |
20.70g |
11.38g |
17.60g |
20.70g |
|
Amino acetic acid (glycine) |
5.66g |
8.76g |
10.30g |
5.66g |
8.76g |
10.30g |
|
L-Arginine |
6.32g |
9.78g |
11.50g |
6.32g |
9.78g |
11.50g |
|
L-Proline |
3.74g |
5.78g |
6.80g |
3.74g |
5.78g |
6.80g |
|
L-Tyrosine |
0.22g |
0.34g |
0.40g |
0.22g |
0.34g |
0.40g |
|
L-Serine |
2.75g |
4.25g |
5.00g |
2.75g |
4.25g |
5.00g |
|
Sodium Acetate |
4.31g |
5.94g |
6.80g |
- |
- |
- |
|
Dibasic Potassium Phosphate |
5.22g |
5.22g |
5.22g |
- |
- |
- |
|
Sodium Chloride |
2.24g |
1.54g |
1.17g |
- |
- |
- |
|
Magnesium Chloride |
1.02g |
1.02g |
1.02g |
- |
- |
- |
Indications: A source of L-amino acids for use in parenteral nutrition regimens for patients unable to absorb adequate oral nutrition. Dosage and Route: For intravenous use through a central venous catheter. The total daily dose of the solution depends upon the patient’s metabolic requirement and clinical response. Administer with non-protein energy source. Consider nitrogen balance. Recommended daily dietary allowances for protein range from 2.2g/kg of body weight for infants to 56g for adults weighing 70kg. The dosage of parenteral nutrition should be individually tailored to the amino acid, electrolyte and energy requirements of the patient. Protect from light when used in neonates and children below 2 years. Side effects: See Summary of Product Characteristics for detail. Unknown frequency - Anaphylactic reactions (including shock), hypersensitivity, pulmonary vascular precipitate. Adverse reactions attributed to parenteral amino acid products include azotemia and to parenteral nutrition with amino acid components include hepatic failure, hepatic cirrhosis, hepatic fibrosis, cholestasis, cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. Precautions: Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid and other hypersensitivity/infusion reactions have been reported – stop infusion immediately if signs/symptoms develop. Pulmonary vascular precipitates have been reported, some with fatal outcomes – excessive addition of calcium and phosphate increases risk. If signs of pulmonary distress stop infusion and initiate medical evaluation. Solution, infusion set and catheter should be checked for precipitates. Infection and sepsis may occur particularly in patients predisposed to infectious complications. Careful symptomatic and laboratory monitoring can help recognise early infections. Heightened emphasis on aseptic technique in catheter placement, maintenance and nutritional formula preparation can decrease occurrence of septic complications. Careful monitoring and slowly increasing fluid intake while avoiding overfeeding can prevent complications of refeeding syndrome. The solution is hypertonic and liable to cause venous irritation at the site of injection if administered peripherally. Monitoring should be appropriate to the patient’s clinical situation and condition, and should include determinations of water and electrolyte balance, serum osmolarity, acid/base balance, blood glucose monitoring and liver and kidney function. Amino acid solutions should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing liver disease or liver insufficiency. Increase in blood ammonia levels and hyperammonemia may occur in patients receiving amino acid solutions, consider discontinuation should symptoms develop. In some patients this may indicate the presence of a congenital disorder of amino acid metabolism or hepatic insufficiency. Blood ammonia should be measured frequently in newborns and infants to detect hyperammonemia, which may indicate the presence of a congenital abnormality of amino acid metabolism. Mixtures containing amino acids may precipitate acute folate deficiency and folic acid should be administered daily. An adequate source of non-protein energy should be administered concurrently if parenterally administered amino acids are to be retained by the body and utilised for protein synthesis. Caution in patients with pulmonary oedema, cardiac and renal insufficiency. There are no adequate data from the use of Synthamin in pregnant or lactating women. Healthcare Professionals should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits for each specific patient before administering Synthamin. Due to generation of peroxides and other degradation products from light exposure, protect from ambient light until administration is completed when used in neonates and children below 2 years. Contraindications: Known hypersensitivity to any of the active substances, excipients, components or container. Congenital abnormality of amino acid metabolism. Synthamin (with electrolytes) must not be administered to patients with clinically significant elevation of plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, magnesium and/or phosphorous. Interactions: Do not add other medicinal products or substances without first confirming their compatibility and the stability of the resulting preparation. Administer Synthamin (with electrolytes) with caution in patients treated with agents or products that can cause or increase the risk of hyperkalaemia. Overdose: Hypervolemia, electrolyte disturbances, acidosis and/or azotemia may occur. In case of overdose, stop infusion immediately. Further intervention may be required if medically indicated. Date of preparation: May 2020.
Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC):
Primene SmPC
Synthamin 9, 5.5% (SmPC)
Synthamin 14, 8.5% (SmPC)
Synthamin 17, 10.0% (SmPC)
Synthamin 9, 5.5% without electrolytes (SmPC)
Synthamin 14, 8.5% without electrolytes (SmPC)
Synthamin 17, 10.0% without electrolytes (SmPC)